Are Flavonoids Antioxidants?
Flavonoids are antioxidants in many foods you enjoy. These natural plant pigments are known to include over 4,000 different compounds and are found in vegetables, fruits, herbs, and many beverages. Flavonoids are now highly recognized for their antioxidant properties and their potential to reduce your risk of certain diseases. [1]
Jump Ahead
Flavonoid Benefits
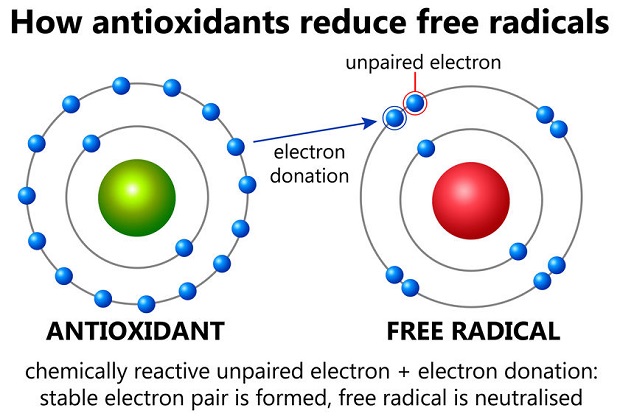
Dietary flavonoids include anthocyanidins, flavan-3-ols, flavonols, flavones, flavanones, and isoflavones, and the effect of each individual compound varies according to its molecular structure. [2] Like all antioxidants, flavonoids may benefit you by helping to protect cells from harmful molecules such as free radicals, peroxides, and metallic ions. [3] Excessive cellular damage caused by these molecules is commonly linked to aging, cardiovascular disease, cancer, autoimmune disease, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. [4] Therefore, the regular consumption of flavonoid-rich foods and beverages is widely thought to help reduce the risk of many diseases and slow the effects of aging. [5]
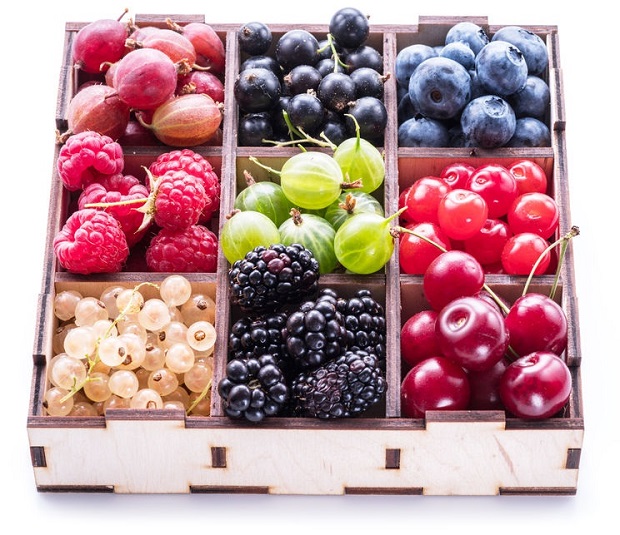
Foods Highest In Flavonoids

Flavonoids are synthesized in significant amounts by various plants inside their flowers, fruits, leaves, and other tissues. [6] Leafy vegetables, onions, citrus fruits, apples, berries, cherries, and soybeans are all important sources of dietary flavonoids. Tea is the primary dietary source in Eastern societies, and wine is the primary dietary source in Western societies. [7]
Surprising Dietary Flavonoid Sources

More recently, it was discovered that hop flowers, used in beer brewing, contain a unique flavonoid compound that shows promise as a cancer preventative. [8] Flavonoids may also be beneficial in other ways: apigenin, a compound commonly found in chamomile tea, peppermint, and parsley, is a known mood enhancer with mild anxiety-reducing properties. [9]
Resources
- [1] Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (ACS Publications) – “Plant Flavonoids, Especially Tea Flavonols, Are Powerful Antioxidants Using an in Vitro Oxidation Model for Heart Disease.”
- [2] Linus Pauling Institute – “Flavonoids.”
- [3] [4] [5] Neha, K.; Haider, M.R.; Pathak, A.; Yar, M.S. “Medicinal prospects of antioxidants: A review.” Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 178, 687–704.
- [6] Ligi, Sergio, et al. “Flavonoids: Overview of Biosynthesis, Biological Activity, and Current Extraction Techniques.” Plants; 2023, 12(14), 2732.
- [7] Alhamzah Hasan Waheed Janabi, Asghar Ali Kamboh, Muhammad Saeed, Lu Xiaoyu, Jannat BiBi, et al. “Flavonoid-rich foods (FRF): A promising nutraceutical approach against lifespan-shortening diseases.” Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Feb; 23(2): 140–153.
- [8] Sosmitha Girisa, Queen Saikia, Devivasha Bordoloi, Kishore Banik, Javadi Monisha, Uzini Devi Daimary, Elika Verma, Kwang Seok Ahn, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara; “Xanthohumol from Hop: Hope for cancer prevention and treatment.” IUBMB Life. Volume73, Issue8; August 2021; Pages 1016-1044
- [9] Psychology Today – “Flavonoids: Antioxidants Help the Mind.“





