Does Carbon Dioxide Dissolve in Water?
Carbon dioxide does dissolve in water. Carbon dioxide dissolves in water to form an aqueous solution. This may seem counterintuitive. Carbon dioxide is a gas, and water is a liquid. However, gases, liquids, and even solids are all chemicals. This means they can all dissolve in solvents. Dissolution creates a homogeneous solution with components derived from solutes and solvents. In this case, water serves as the solvent, and carbon dioxide serves as the solute. The reaction is a favorable one, which produces carbonic acid.
Like Dissolves Like: A Rule of Thumb
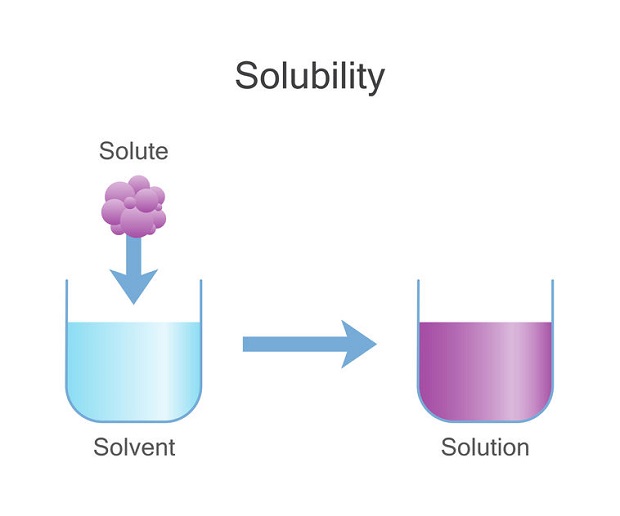
A basic rule in chemistry is “like dissolves like.” This is often interpreted to mean solute-solute reactions and solvent-solvent interactions occur first. These reactions must be broken before solute-solvent interactions can take place. This necessitates energy. Afterward, solute-solvent interactions can develop and release energy. If the released energy is greater or equal to the amount required to break solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions, then solute-solvent interactions will occur spontaneously. According to this rule, carbon dioxide is not likely to dissolve in water.
Entropy: The Unspoken Component

“Like dissolves like” is a rule of thumb, but it is not the complete story. Entropy is also involved. In situations where pressure and temperature can change, entropy can and does drive reactions even though these interactions seem to contradict “like dissolves like.” This is why pressure is required to make carbonated beverages.
Carbon Dioxide in Water: Amounts May Vary
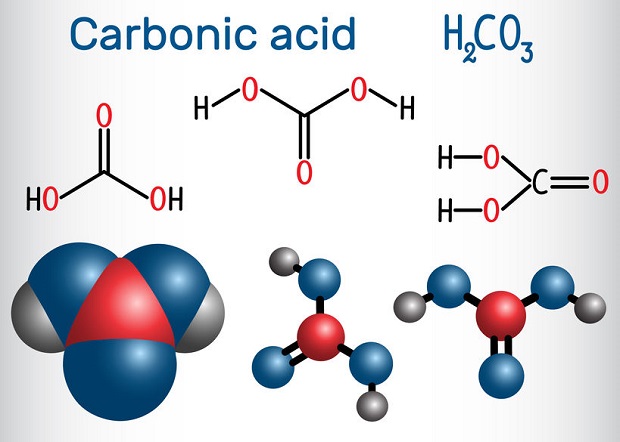
The amount of carbon dioxide that dissolves in water is dependent upon several factors. These include temperature, pressure, and pH. Reactions attempt to achieve equilibrium. In this case, equilibrium is not a concentration quantification. It is an equalization between the forward and reverse reaction rates. When the reaction achieves equilibrium, the concentrations of carbon dioxide, water, and carbonic acid can be related by a mathematically derived ratio known as the equilibrium constant. However, actual amounts will need to be assayed.
Glossary of Terms

Aqueous Solution: a solution in which water is the dissolving medium or solvent.
Biology-online.org
Dissolution: the process by which a solute forms a solution in a solvent.
Solvent: the component whose phase is retained when the solution forms; if all components are the same phase, the one in the greatest amount is the solvent. If one of the components is water, water is always the solvent.
Oklahoma State University
Solute: dissolved substance; especially: a component of a solution present in a smaller amount than the solvent.
Merriam-Webster Dictionary
Expert Opinion

“The maximum total amount of CO2 that may dissolve in water is a function of pH. This is because as pH changes, the fraction of the total dissolved Co2 as Co2 (aq) also changes.”
Dissolved Carbon Dioxide Utah State University
Resources
- OSU Department of Chemistry – Chem 1125 Chapter 15
- Encyclopedia Britannica – Carbonic Acids and Carbonic Salts
- US Department of Energy- Ask a Scientist – Dissolving Carbon Dioxide into Water
- Utah State University – Dissolved Carbon Dioxide
- University of California Davis-Physical Chemistry – The Equilibrium Constant