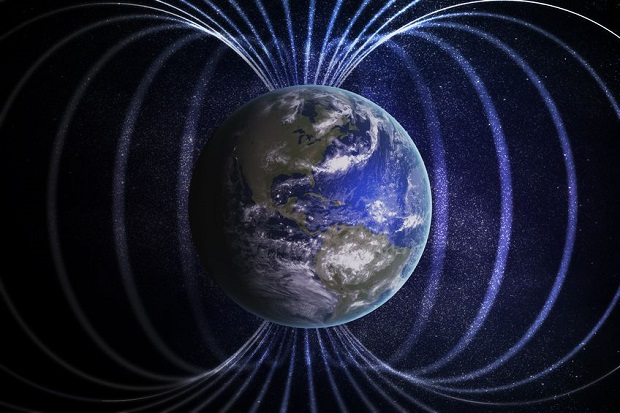
Does the Earth Have a Magnetic Field? The Earth does have a magnetic field originating in the Earth’s core. The Earth has a magnetic field surrounding it, high above the atmosphere. The magnetic field allows compasses to work, as it forces the needle to point towards the magnetic north.
Origin of the Magnetic Field
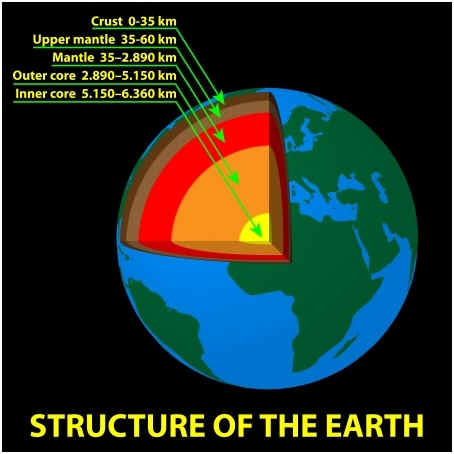
The magnetic field originates in the Earth’s core. As you may know, the Earth’s core is made of iron, which has magnetic properties. This iron is under such high pressure that it’s actually molten. The shifting of this iron helps generate the field, and it also slowly shifts its position. This shifting makes the field eventually reverse at random intervals. The field stretches out from the core out into what is called the magnetosphere. The magnetosphere is thousands of kilometers above the surface. Because the flow of iron isn’t consistent, the magnetic field truly isn’t either. Its strength ebbs and flows depending on its position.
Purpose of the Magnetic Field
The magnetic field’s primary purpose is to protect the Earth from bombarding solar winds. Solar winds result from the sun’s nuclear processes and could potentially damage the entire planet’s ozone layer. The magnetic field protects the ozone layer. The ozone layer, in turn, protects the planet’s ecology and life forms. In this way, the magnetic field indirectly protects life on Earth. This devastating process has been seen on Mars, as scientists believe that its lack of magnetic field made it become the barren, rust-colored wasteland it is today.





