Does the Moon Orbit the Earth? The Moon does orbit the Earth. It takes 27.322 days for the moon to travel completely around the Earth. The moon travels around the Earth in an elliptical orbit, causing its rotation to slow when it is closest to Earth.
History of Moon’s Orbit Around Earth

The Moon and the Earth have been connected in their orbits around the sun for over four billion years. The gravity and orbit of each celestial object affect the other. The Earth is only about thirty million years older than the Moon, and when the Moon first formed, it was ten to twenty times closer to Earth than it is now. This closeness of the Moon and Earth in the early evolution of our planet is likely the cause of plate tectonics in the Earth’s crust, forming the continents and landmasses of the Earth. The Moon’s gravity and orbit continue to affect Earth’s life through total eclipses, ocean and river tides, and phases of the Moon.
Does the Face of the Moon Change?

The Earth’s moon is large as planetary satellites go. Its size and distance from Earth have several effects. One is that the Moon and Earth have traded energy over millions of years as they orbit together. The Moon’s gravity has slowed the speed of the Earth’s rotation, and the Earth’s gravity has increased the speed of the Moon’s rotation. Over millions of years, the two bodies have become synchronous in their orbits, with the Moon always showing only one side toward the Earth.
The size of the Moon and its distance from Earth also result in the Moon and Sun appearing to be about the same size in the sky, although the Moon is actually millions of times smaller than the Sun. Because the Sun and Moon appear to be the same size, the result is a total lunar eclipse when the Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun. The existence of lunar eclipses has profoundly affected the development of many myths and religions globally.
Ocean Tides and the Moon
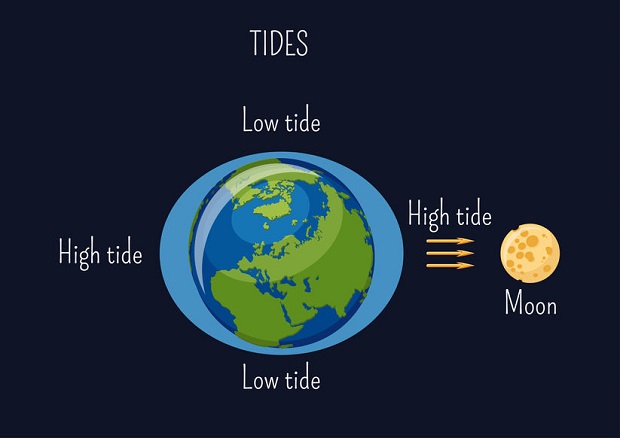
The force of gravity becomes weaker as distance increases. The Moon’s gravity has a stronger effect on the Earth’s side, closer to the Moon. Because the Moon orbits around the Earth slightly faster than the Earth orbits on its own axis, the Moon pulls a bulge of water in the ocean around it.
This bulge of ocean water creates ocean and river tides. With the tides, the water level rises and falls between one and ten meters several times a day along coastlines and in river estuaries. This creates environmental and ecological conditions important to many forms of oceanic and terrestrial life.
Phases of the Moon

Also, because the Moon orbits the Earth slightly faster than the Earth rotates on its own axis, the Moon goes through phases. In the course of a month, the moon will go from full moon to crescent moon to new moon. The Moon’s orbit’s speed relative to Earth’s orbit causes the Moon to advance in the sky hour by hour and day by day relative to the fixed stars in the background.
As this progression moves along, the percentage of the Moon, which is illuminated by the sun, changes, creating the phases of the Moon. The existence of lunar phases gave humanity an important way of tracking time and led to crucial advances in agriculture and civilization’s history and development.