How Far Is Earth from the Sun?
The average distance at which Earth orbits the sun is 92,955,807 miles. However, this number is variable, as the Earth revolves around the sun in a slightly elliptical orbit. Earth is only about 91 million miles from the sun in January, while in July, our planet’s center is about 94.5 million miles from the sun’s center. [1]
Jump Ahead
- Earth’s Orbit Affects Distance from the Sun
- How Does Our Distance from the Sun Affect Earth?
- Reason for the Season’s
Earth’s Orbit Affects Distance from the Sun
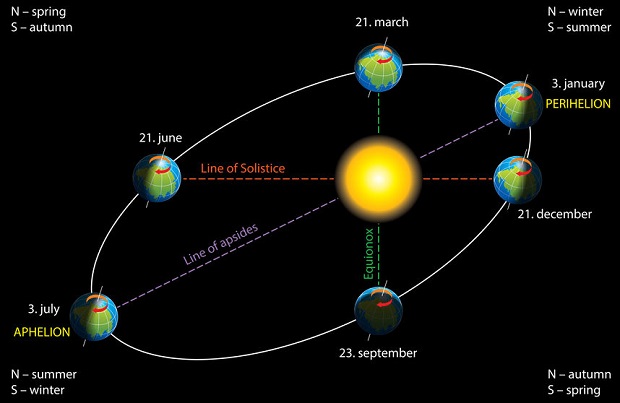
The Earth’s slightly elliptical orbit around the sun creates perihelion and aphelion. This means that at perihelion (the point where Earth is closest to the sun, which always happens in January), the Earth’s center is only about 91 million miles from the sun’s center. Since the orbit is elliptical, there is conversely a point at which the center of the Earth is furthest from the sun’s center – the aphelion. Aphelion occurs yearly in July when our planet’s center is about 94.5 million miles from the sun’s center. [2]
As you can see, this is only a difference of about 3.5 million miles. Though the difference seems substantial, it only equates to slightly more than 3%. In fact, this 3% difference is virtually imperceptible to the human eye when comparing this orbital ellipse to an ordinary circle.
How Does Our Distance From the Sun Affect the Earth?
When discovering that our distance from the sun is variable, some think that this is the cause of the seasons. This conclusion seems logical, but it is mistaken. The change in distance is so minute that it has a minimal actual effect on climate. It does have some effect – however, this is negligible. The Earth is slightly cooler at perihelion and slightly warmer at aphelion. [3]
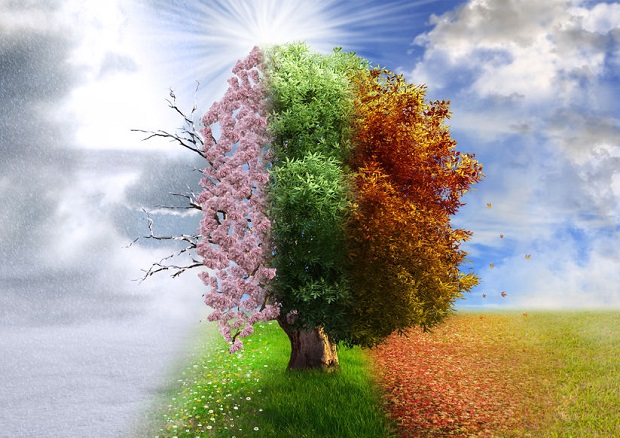
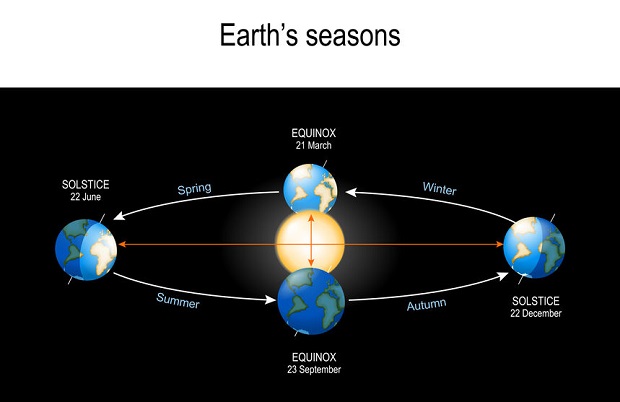
Reason for the Seasons
The real reason for the seasons is, in fact, the result of the tilt of the planet’s axis. This can be understood by imagining that a straight line runs through the Earth’s center from the North Pole to the South Pole. This imaginary line through the poles is not vertically straight up and down but at a diagonal of roughly 23 degrees. This tilt causes the northern hemisphere to receive more sun than the southern hemisphere at certain times of the year and vice versa. [4]
This planet’s tilt is also responsible for a day lasting 24 hours. The Earth spins on this axis toward the sun during the day and away from the sun at night. The spin rate is why one whole day lasts exactly 24 hours. If you look at any quality globe, you will see that it is tilted just like it is in reality, as viewed on an axis from space. [5]
Resources
- [1] [2] Space.com “Astronomical Unit: How Far Away Is the Sun?“
- [3] NASA Science – “Earth at Perihelion“
- [4] NASA Science – “What Causes the Seasons?“
- [5] Space.com – “Why is Earth’s day 24 hours long?