How Is Precipitation Measured?
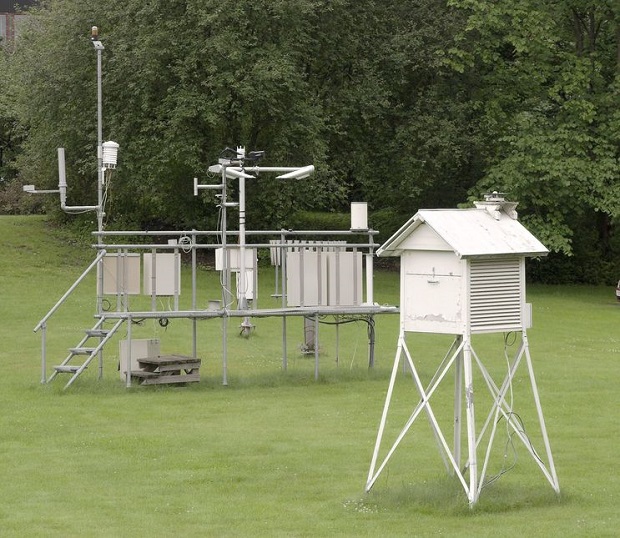
Precipitation is measured by collecting it in a rain or snow gauge as it falls or by measuring the amount of snow that is present on the ground. Precipitation can also be estimated by analyzing data from radar images. Accurate precipitation information is important when examining climate trends, forecasting stream, and river flooding, and determining snow depth.
Rainfall Measurement
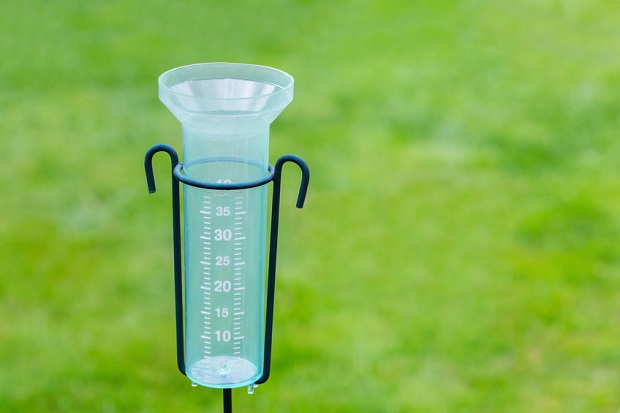

Cylindrical rain gauges can be found at most hardware and home stores. These gauges provide a level of accuracy that is adequate for home rainfall measurement. More advanced rain gauges include data recording capability and can be used to measure large quantities of rainfall that a household rain gauge cannot measure. It is important that any rain gauge is located far from buildings and tall vegetation.
Snow and Frozen Precipitation Measurement

Snow and other frozen precipitation are measured in one of two ways. One way snow is measured is by placing a snowboard on the ground before any snow falls. The board should be located in an area where it will not be disturbed by humans or animals and where the snow is unlikely to be blown into drifts. After a snowfall event, a ruler or yardstick can be pushed into the snow until it reaches the board to measure the depth of the snow. The snowboard can then be moved to the top of the snow and used again to measure new snowfall. Snow gauges are also used to collect snow as it falls. The collected snow is melted and measured to find the equivalent amount of liquid in the snow.
Radar Estimation to Measure Precipitation

Radar images can be used to measure precipitation by observing a quality called reflectivity. Reflectivity occurs when individual precipitation particles are captured as backscatter on a radar image. The reflectivity can be used to calculate the precipitation rate in that area. Radar estimation is particularly useful when gathering precipitation data over a large area and can measure rain and frozen precipitation.
Resources
National Weather Service – “Point Precipitation Measurement, Areal Precipitation Estimates And Relationships to Hydrologic Modeling“
National Weather Service – “Snow Measurement Guidelines for National Weather Service Surface Observing Programs“
Community Collaborative Rain, Hail, & Snow Network – “In Depth Snow Measuring“