Is Earth Bigger Than Mercury? Earth is bigger than Mercury. Mercury is notably smaller than the Earth. You may wonder just how much smaller it is compared to Earth, and there are several ways to compare the two. We’ll incrementally go down the many possible comparisons to truly grasp the vast differences between the two planets. That way, you’ll be able to grasp truly and appreciate just how massive our world is compared to Mercury.
Mercury’s Diameter vs. Earth
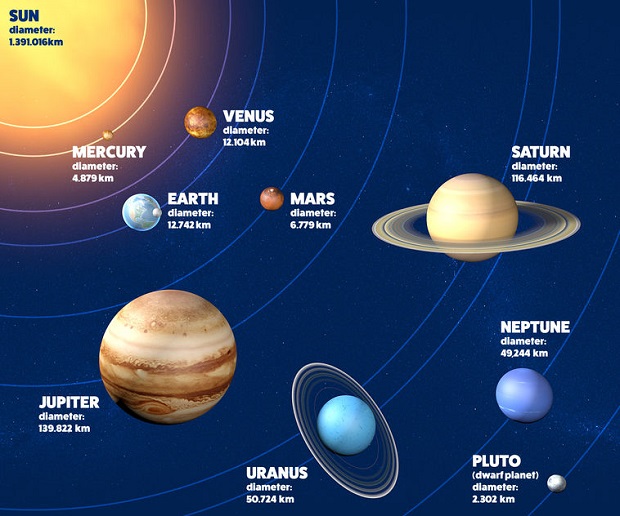
The diameter of a planet is a great way to understand its basic size. The diameter is measured by imagining a line that perfectly bisects the planet. Mercury’s diameter is roughly 38% that of Earth’s. This means that if you line up three Mercuries, you would find that this combined diameter is barely larger than a single Earth’s.
Mercury’s Mass vs. Earth

Of course, size isn’t everything in the cosmos. The largest, most destructive single objects in the universe (black holes) are caused by some of the smallest things in existence. The difference is that these objects’ masses are gargantuan.
Mercury, however, isn’t. According to NASA (the National Aeronautics and Space Administration), Mercury has roughly one-twentieth the Earth’s mass. If you were to do the math, you would find that this means its mass is about 5% of ours.
Mercury’s Density vs. Earth
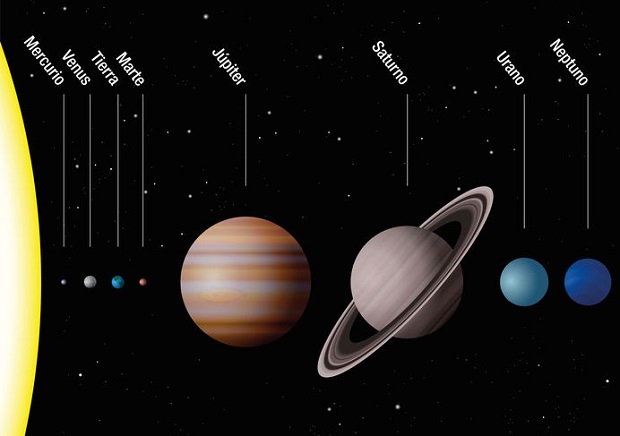

This combination individually demonstrates Mercury’s diminutive status compared to our world, and the combined measure also adds light to just how small it is.
If you know the size of an object (easily calculated from its diameter) and its mass, you’ll be able to find its density. This measures how much mass is stuffed into the amount of space available. Objects with a high density include neutron stars, certain asteroids, and some planets.
Mercury, however, is not one of them. The density of the planet is still less than that of the planet Earth.